You've probably heard of the Russian, the Mongol, the Roman, the British and a few other empires. Until pretty recently, they were all over the place (literally). So, what were the largest empires in history?
Advertisement

You've probably heard of the Russian, the Mongol, the Roman, the British and a few other empires. Until pretty recently, they were all over the place (literally). So, what were the largest empires in history?
Advertisement
These continent and century-spanning entities had a great deal of impact on the social, political, cultural and economic conditions of their times. The bigger they were, the more they left an impression on the world. Here are some of the most historically influential.
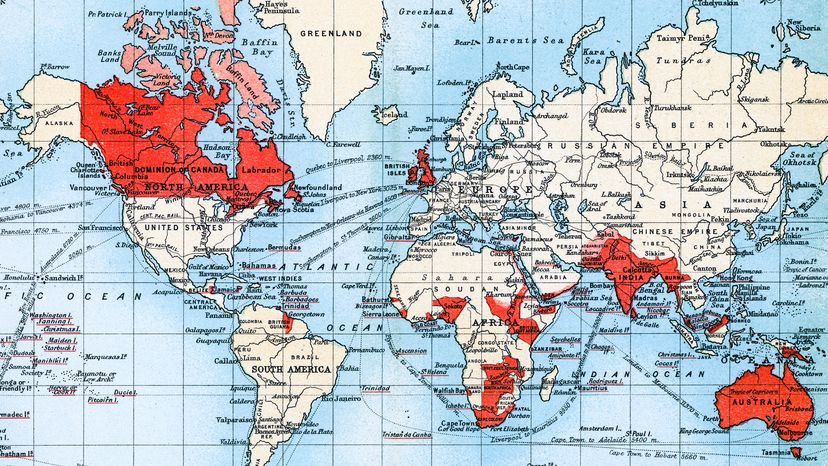
At its height, the British empire covered 13.7 million square miles (35.5 million square kilometers) That's around 24 percent of the world's land area. It was a maritime empire, meaning it stretched across oceans and seas. The British Empire lasted around 400 years, making it long-lived, as well.
Advertisement
As the British were very fond of saying, back in their imperial heyday, "the sun never sets on the British Empire." At its height, it stretched from Great Britain to huge swaths of Africa, much of the Indian subcontinent, Oceania, parts of North America and the Caribbean.
Besides all of this land and ocean trading routes, it also meant that close to a quarter of the world's population at the time was under the sway of the British Empire.
The end of the British Empire came with the Second World War. Despite being on the winning side of Word War II, British society was heavily damaged, and the new order that emerged shifted power decisively to the United States. (One of Britain's former colonies! Funny how that works.)
The Mongol empire gets the distinction of the largest contiguous land empire in history. That means it was the largest empire whose territories were all connected via landmass — 9.3 million square miles (23 million square kilometers) of land, in fact.
The Mongols weren't that big on ocean expeditions, but they were excellent horsemen, which meant that they could invade quickly and over a wide range of territories.
Founded by Genghis Khan in 1206, the Mongol empire lasted until the 14th century. At its height, it stretched across the entirety of Asia, include parts of the Middle East, and into Eastern Europe.
While the Mongols had a reputation as swift and brutal conquerors, they were also skilled administrators, effectively governing their vast territories from the steppes of Central Asia.
The Russian Empire was also very big. In fact, it was second only to the Mongol Empire in terms of contiguous land conquered and ruled over, at 8.8 million square miles (22.8 million square kilometers).
The Russian Imperial dynasty lasted from 1721 until the Russian revolution of 1917, where the ruling family was finally overthrown and the Soviet Union was established.
Unlike the British Empire, the Russian Empire didn't come through the Industrial Revolution quite so successfully. Instead, unrest over various issues — including the status of the serfs, who were held in a kind of bondage by the landowning class — culminated in the revolutionary upheavals of 1917.
"I claim this land for Spain!" is a phrase you didn't want to hear if you were anywhere on Earth during the long reign of the Spanish empire.
Indeed, many cultures and ethnic groups were severely damaged, if not outright exterminated, by the Spanish conquerors. Beginning in the end of the 15th century, the Spanish Empire covered nearly 7 million square miles (18.1 million square kilometers) at its peak.
The Spanish Empire boasted exceptional naval capabilities; this, combined with the ruthlessness of its explorer clients (Columbus, Cortes, Pizzaro), led to the establishment of far-flung colonies.
As in many cases, ruling over the vast territories they had conquered eventually proved too daunting. Combined with political and economic problems at home, the Spanish Empire had mostly faded from world history by the 19th century, although it didn't officially end until 1976.
The Qing dynasty was the last great imperial dynasty of China. At its height, its vast territories covered 5.68 million square miles (14.7 million square kilometers) of land. That includes present day Mongolia, Tibet, China, Taiwan and other territories.
The Qing dynasty relied upon an extensive, rigorous bureaucratic apparatus that was highly effective at administrating its empire, which had been conquered via superior military prowess. Over time, however, international relations became strained, and internal pressures created violent unrest.
The Roman Empire lasted from 27 B.C.E. to 476 C.E., about 500 years. At the height of its dominance, it covered 1.9 million square miles (5 million square kilometers), including swaths of North Africa, the Middle East, and much of present-day Europe.
That's significantly less land than some of the other empires in history, but its enormous influence on subsequent societies makes it important to mention.
Much of the modern world's legal system, including our notion of private property, comes from Roman law. The use of Latin influenced many languages that are spoken by hundreds of millions of present-day humans. Aspects of Roman culture, from governance to engineering and architecture, continues to influence present-day Western society.
Advertisement
An empire is defined as a group of countries or states that are controlled by one leader or government. In practice, this means that an empire controls a lot of territory — and the people living within that territory.
Inevitably, this control entails enormously complex social, political, religious, military, and economic organization.
Advertisement
Empires always got bigger via force, and the establishment of many "great" empires in history meant enormous human suffering. But once established, there was a range of different experiences within those empires, sometimes involving relative peace and prosperity. In the end, no two empires are exactly alike, as we'll see in the subsequent sections.
Empires, as noted above, are large. Very large. We're talking about millions of square miles of territory. Since we're talking here about "largest empires in history," we paid particular attention to the vast distances covered by land (and in some cases, water).
But there are other ways to look at an empire. Sometimes, as in the case of the Roman empire, it might not cover as much ground, but its influence is enormous. Empires have a way of influencing each other, of setting up the conditions for later empires in history.
Advertisement
As you can see, we looked at the largest and the most consequential to human history.
Please copy/paste the following text to properly cite this HowStuffWorks.com article:
Advertisement